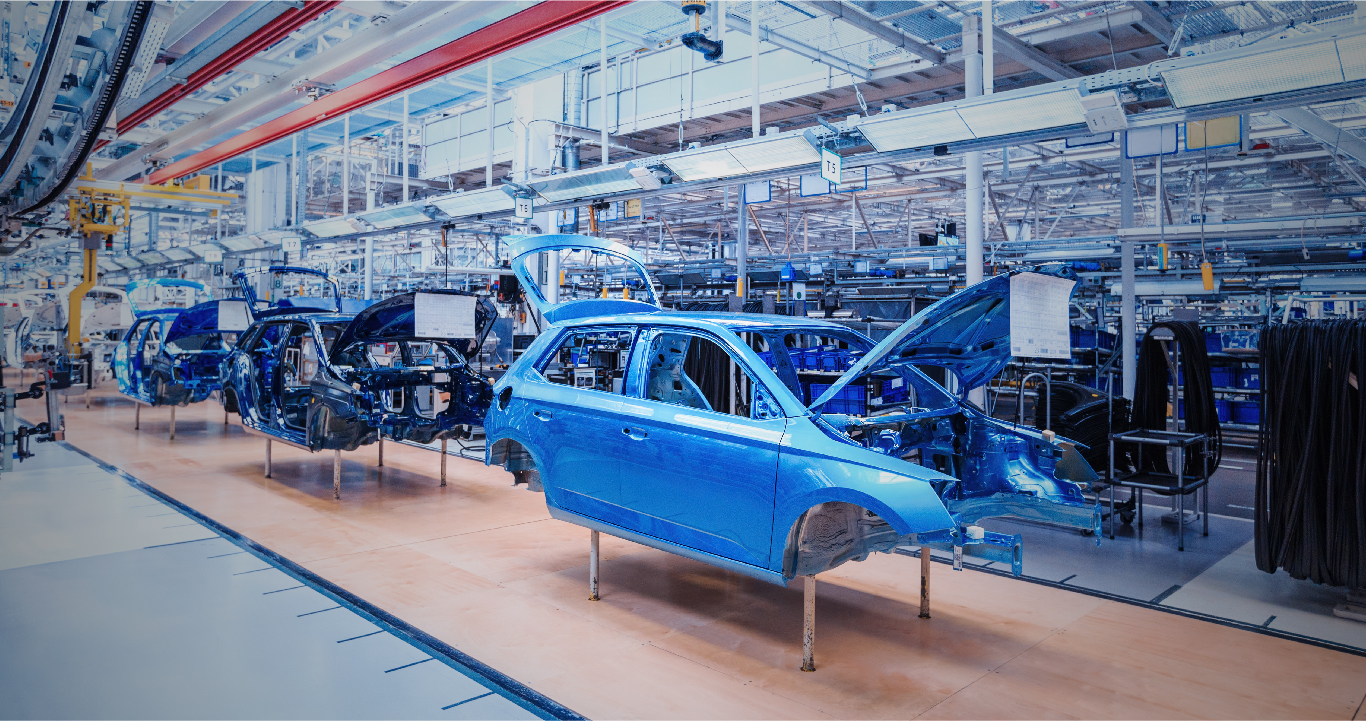
Use Traceability to Avoid that Million-Dollar Loss in your Automobile Manufacturing Unit
Whether it’s surface, water or air, nowhere is safety more important than in the transport industry. Vehicle safety gained importance by way of law in 1966 – the 49 USC Chapter 301 – Motor Vehicle Safety Act whereby each automobile manufacturer is required to recall or repair any new vehicle with safety defects or issues, free of charge.
The consequences of product recalls have caused significant financial and reputational damage. Some of the more recent recalls have been Ford (2019), Mazda and Toyota (2018), and Mercedes Benz (2017).
The Motor Vehicle Safety Act was made more stringent with the Transportation Recall Enhancement, Accountability, and Documentation (TREAD) Act in 2000, making traceability a must in the automobile industry.
Countries around the world followed suit with locally tweaked legislation mandating traceability. Manufacturers in the US and Europe use the ISO/TS 16949 Standard on their suppliers for quality compliance. Against this background, traceability of parts is being implemented in the automobile industry.
Stages of Traceability
Shipment & Customer Traceability

Even after a new automobile has left the factory, it needs to be tracked till it is handed over to the next transit point which may be a shipment yard or a distributor, or ideally till it is handed over to the customer. For this, traceability systems must be driven across all transit points.
A customer complaint system should be able to capture, manage and resolve for review and escalation of product defects and service issues in a simplified manner.
Traceability Information
Each recall of an automobile involves cost – both in terms of money and reputation. Warranty concerns and pre-delivery failures have resulted in huge payouts as claims annually. Ideally, traceability should be able to trace back from warranty claims to the root cause and recover as quickly as possible. This requires more transparent information at each stage, including cost implications.
A more recent development in traceability has been research in applying blockchain technology to capture a more complete information at each stage of automobile manufacture. With more advanced vehicles such as the EVs which use many controls, the need for robust traceability has become more acute today.
Types of Marking Technology used for Traceability 
Parts manufacturers use various methods to mark the parts produced and the decision is based on the actual requirement, and which option fits them financially while also meeting the stringent traceability requirement.
For instance, dot peen marking technology for permanent marking uses a tungsten carbide pin to mark the surface with text and barcodes. Electrochemical etching makes a permanent high-resolution marking on conductive metal surfaces for serial numbers and codes such as barcodes. Various types of laser marking systems for die cast items are capable of withstanding harsh environments.
The printing and labelling at different stages of the supply chain use strong adhesive and strong face surface which enable them to be weather-proof, oil-resistant, car fluid-resistant and pressure-sensitive.
These marking systems can be integrated with databases and software for system-wide traceability. Not to mention, the packaging uses corresponding barcode labels and RFID tags for warehouse traceability.
MELSS has devised many traceability solutions for various industries after thoroughly discussing needs with each manufacturer. We provide complete solutions comprising tools such as barcodes, RFID or NFC along with system-wide information visibility using the software component, and the solutions are IIoT-friendly too.